本帖最后由 hunter33434 于 2016-8-19 14:53 编辑
问题导读:
1.openstack现阶段计费项目情况?
2.需要怎样的环境实现?
3.在没有cloudkitty的情况下如何实现?
4.最终的流程图是什么?
前言:
OpenStack有个比较年轻的费用统计项目CloudKitty,但是它需要与Ceilometer进行结合。在实际的生产环境中,若整个集群资源不大(10台服务器以下)且服务器性能较低,不建议上ceilometer,我的想法主要是mongoDB数据量太大,且会影响前端dashboard拿ceilometer的监控数据,国内主流做OpenStack的公司上ceilometer项目的较少,大部分使用collectd等主流轻量级监控插件。
鉴于此情况,本文主要阐述在没有安装Cloudkitty以及Ceilometer情况下计费功能的实现。
核心思想:
本文描述的计费功能主要是通过虚拟机的vcpu、ram、disk来统计费用。
Nova(Mitaka):
在开始代码之前我们来了解一下nova写表的机制:每一次通过client对云主机进行操作即使用nova命令时,/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/nova/objects/instance.py文件中的save方法进行参数处理,部分代码如下:
def save(self, expected_vm_state=None,
expected_task_state=None, admin_state_reset=False):
"""Save updates to this instance
Column-wise updates will be made based on the result of
self.what_changed(). If expected_task_state is provided,
it will be checked against the in-database copy of the
instance before updates are made.
:param:context: Security context
:param:expected_task_state: Optional tuple of valid task states
for the instance to be in
:param:expected_vm_state: Optional tuple of valid vm states
for the instance to be in
:param admin_state_reset: True if admin API is forcing setting
of task_state/vm_state
"""
# Store this on the class because _cell_name_blocks_sync is useless
# after the db update call below.
self._sync_cells = not self._cell_name_blocks_sync()
context = self._context
cell_type = cells_opts.get_cell_type()
if cell_type is not None:
stale_instance = self.obj_clone()
cells_update_from_api = (cell_type == 'api' and self.cell_name and
self._sync_cells)
if cells_update_from_api:
def _handle_cell_update_from_api():
cells_api = cells_rpcapi.CellsAPI()
cells_api.instance_update_from_api(context, stale_instance,
expected_vm_state,
expected_task_state,
admin_state_reset)
updates = {}
changes = self.obj_what_changed()
for field in self.fields:
# NOTE(danms): For object fields, we construct and call a
# helper method like self._save_$attrname()
if (self.obj_attr_is_set(field) and
isinstance(self.fields[field], fields.ObjectField)):
try:
getattr(self, '_save_%s' % field)(context)
except AttributeError:
LOG.exception(_LE('No save handler for %s'), field,
instance=self)
except db_exc.DBReferenceError as exp:
if exp.key != 'instance_uuid':
raise
# NOTE(melwitt): This will happen if we instance.save()
# before an instance.create() and FK constraint fails.
# In practice, this occurs in cells during a delete of
# an unscheduled instance. Otherwise, it could happen
# as a result of bug.
raise exception.InstanceNotFound(instance_id=self.uuid)
elif field in changes:
if (field == 'cell_name' and self[field] is not None and
self[field].startswith(cells_utils.BLOCK_SYNC_FLAG)):
updates[field] = self[field].replace(
cells_utils.BLOCK_SYNC_FLAG, '', 1)
else:
updates[field] = self[field]
即每对instance进行一次操作,save方法都会对这次操作即update进行一次处理并写入mariaDB表,而改变的状态则在obj_what_change中:
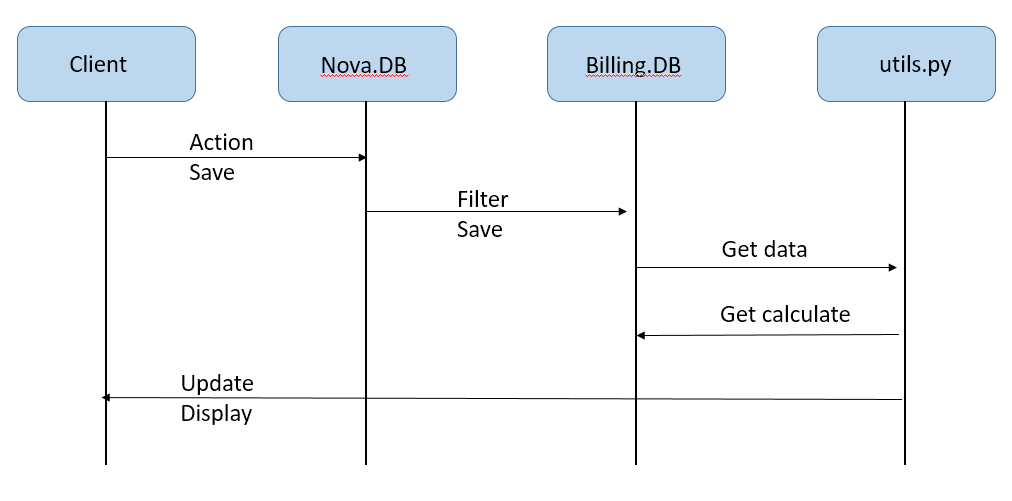
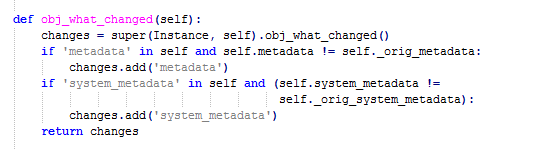 由此可见,我们只需要在client对instance进行操作时,nova在将update信息写入mariadb之前将信息过滤并进行处理同样写入一张billing表即可!
由此可见,我们只需要在client对instance进行操作时,nova在将update信息写入mariadb之前将信息过滤并进行处理同样写入一张billing表即可!
接下去就很简单了
如何实现??
1.在mariadb中创billing的表及用户
mysql -uroot -pMARIADB_PWD <<EOF
drop database if exists billing;
create database billing;
grant all privileges on billing.* to "billing"@"localhost" identified by "BILLING_PWD";
grant all privileges on billing.* to "billing"@"%" identified by "BILLING_PWD";
flush privileges;
EOF
2.初始化表
在这里使用了python的mysql工具包sqlalchemy(http://www.sqlalchemy.org),可以直接通过python语言来定义mysql库及表。
a.init_db.py(DB中数据的状态记录以及使用记录初始化)
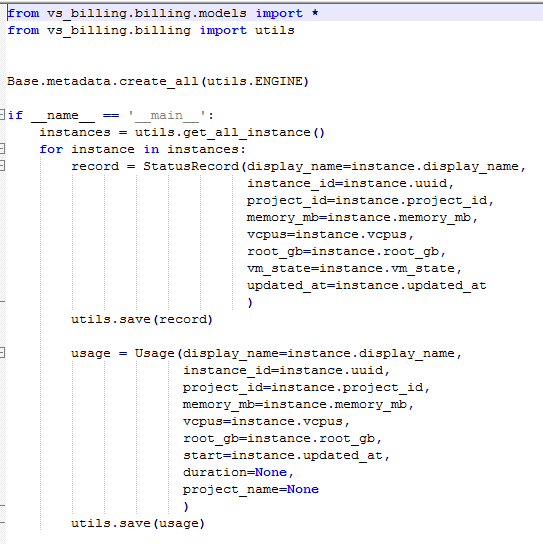
b.utils.py(主要是从billing表中拿数据并计算写入billing表)
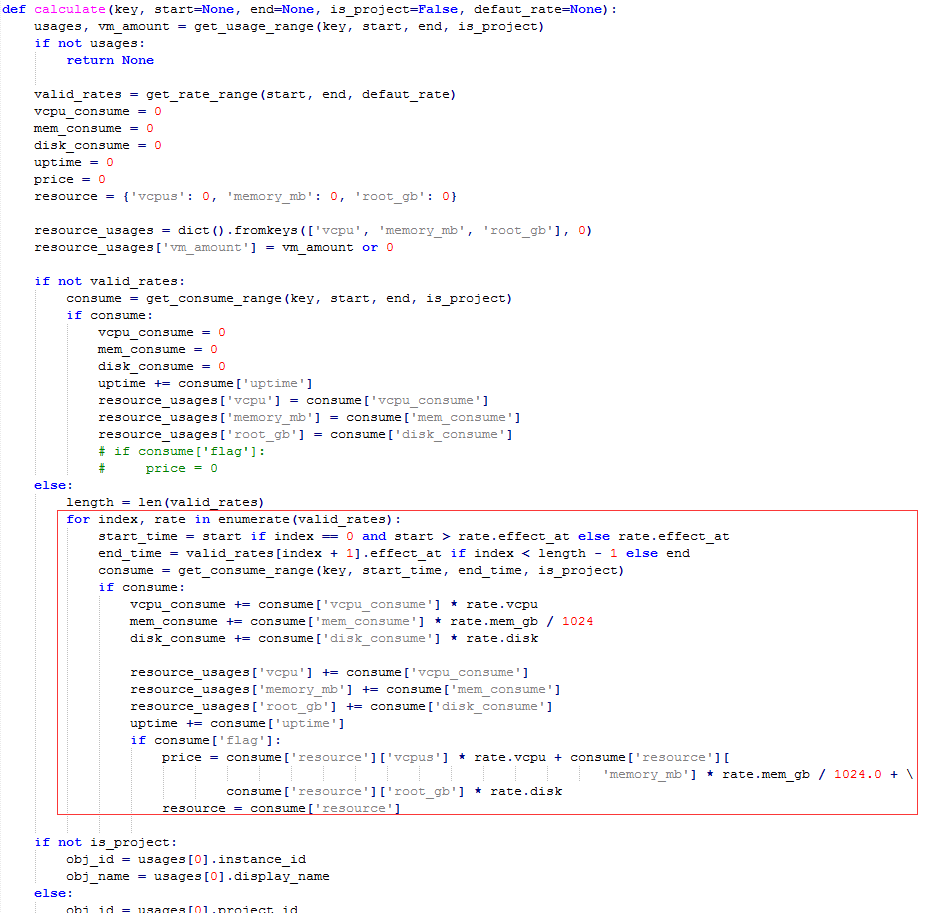
在/etc/nova/nova.conf配置一下billing的参数:
db_connection = mysql://billing:openstack@127.0.0.1/billing
pool_recycle = 600
c.modules.py(定义billing表的title即里面数据的声明,三张表分别是Rate(单价)和Usage(使用量)和StatusRecord(状态记录))
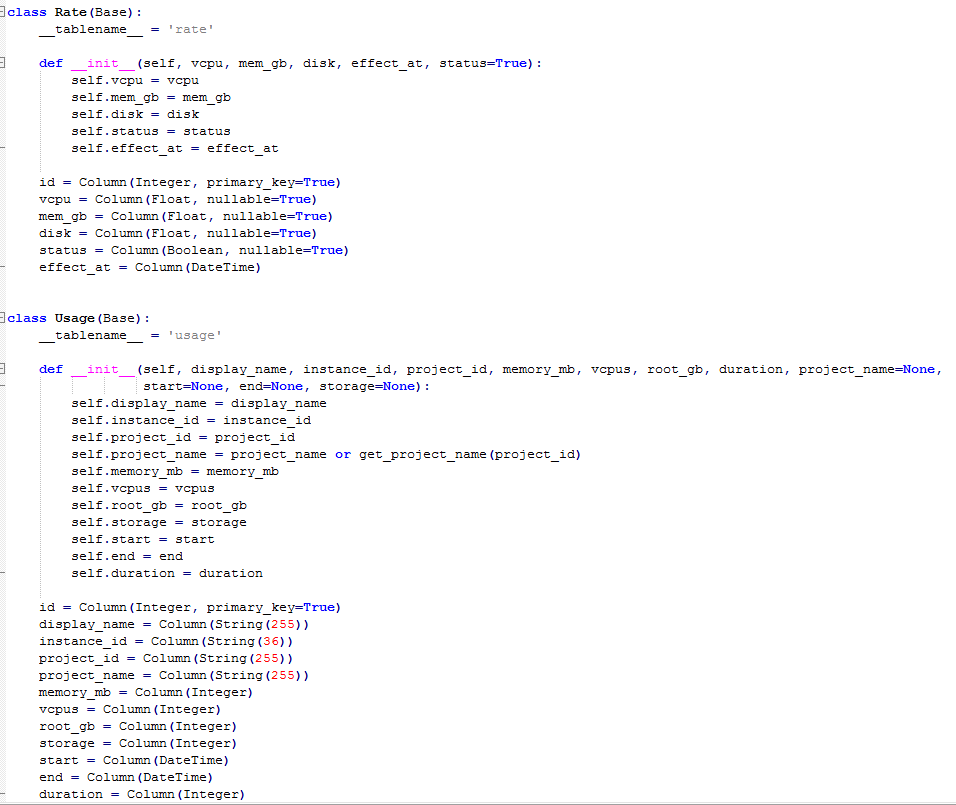
3.Analysis
总体的设计思路是-----
1.部署时先python utils.py跑一遍代码,之后每通过client对云主机进行关机、删除、创建、迁移操作时会记录到billing表中;
2.可以在前端自定义费用模板(也可以直接写进billing.rate表中),后端可以拿到前端传过来的模板信息(rate.cpu、rate.ram、rate.disk)进行计算整合写入表并传给前端
4.WorkFlow
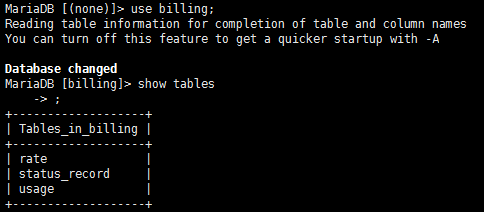
5.DB
billing中有三张表,对应的是价格、状态记录和使用量


本文主要对billing功能进行前瞻,下一节主要讲计算api utils.py文件
计费功能最重要的是理清楚nova中虚拟机状态的变化,create, update,delete,resized等等,只要搞清楚里面的逻辑,对计费的计算一下就能搞清楚了。
|  /2
/2 