|
问题导读
1、如何获取nova service数据库表所有数据?
2、怎样检测服务是否为alive?
3、怎样判断服务状态呢?

环境:centos6.5 openstack ice版
1、

2、

3、
复制代码
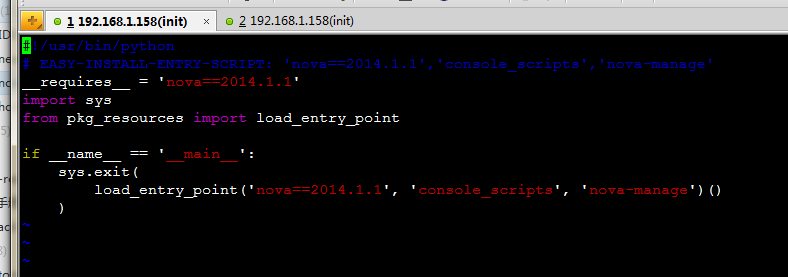
- load_entry_point('nova==2014.1.1', 'console_scripts', 'nova-manage')()
- 第一个参数定向到 /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/nova-2014.1.1-py2.6.egg-info/
然后搜索EGG-INFO/entry_points.txt
- vim /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/nova-2014.1.1-py2.6.egg-info/entry_points.txt
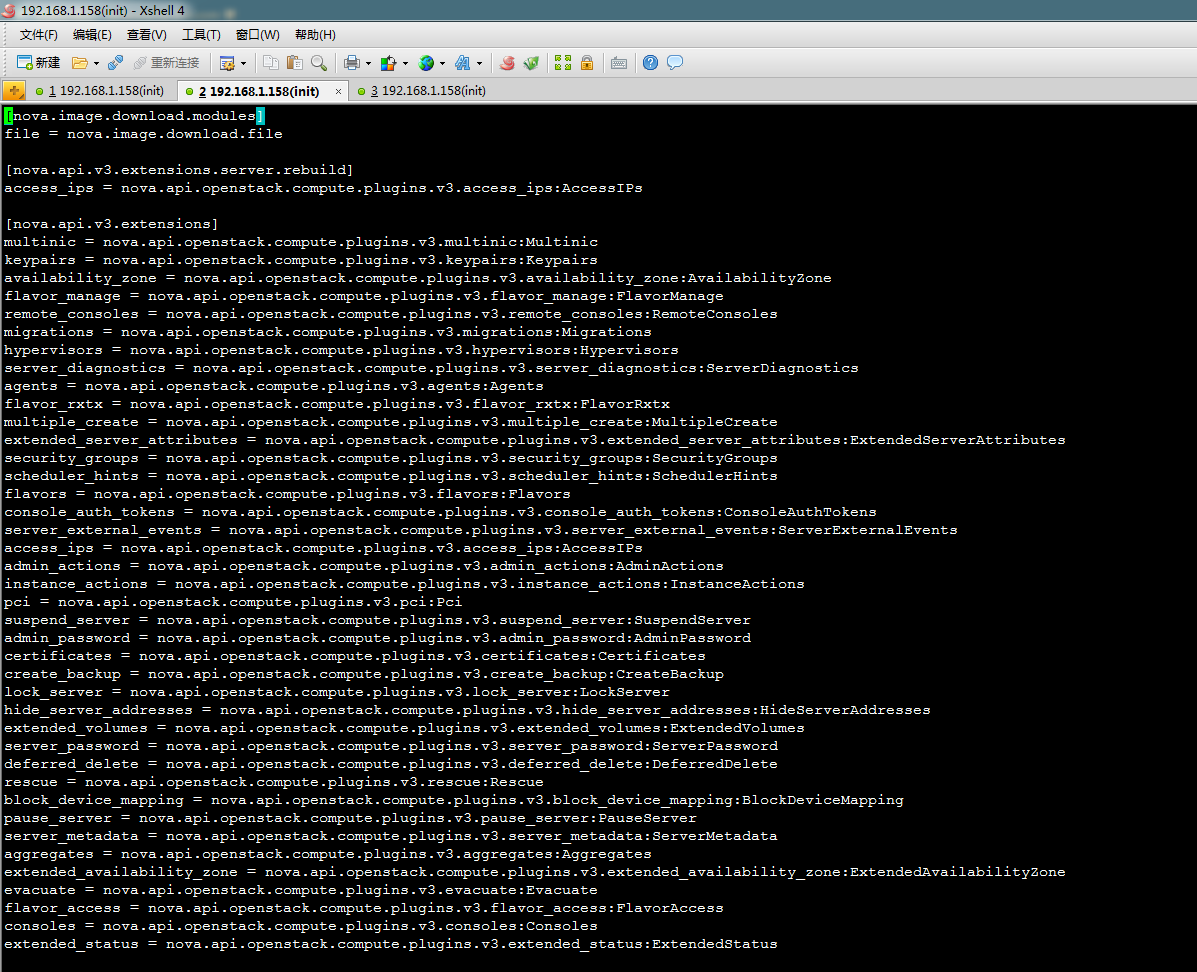
搜索
- load_entry_point('nova==2014.1.1', 'console_scripts', 'nova-manage')()
第二、第三个参数:
- console_scripts、nova-manage
得到入口地址为:
- nova-manage = nova.cmd.manage:main
4、
5、
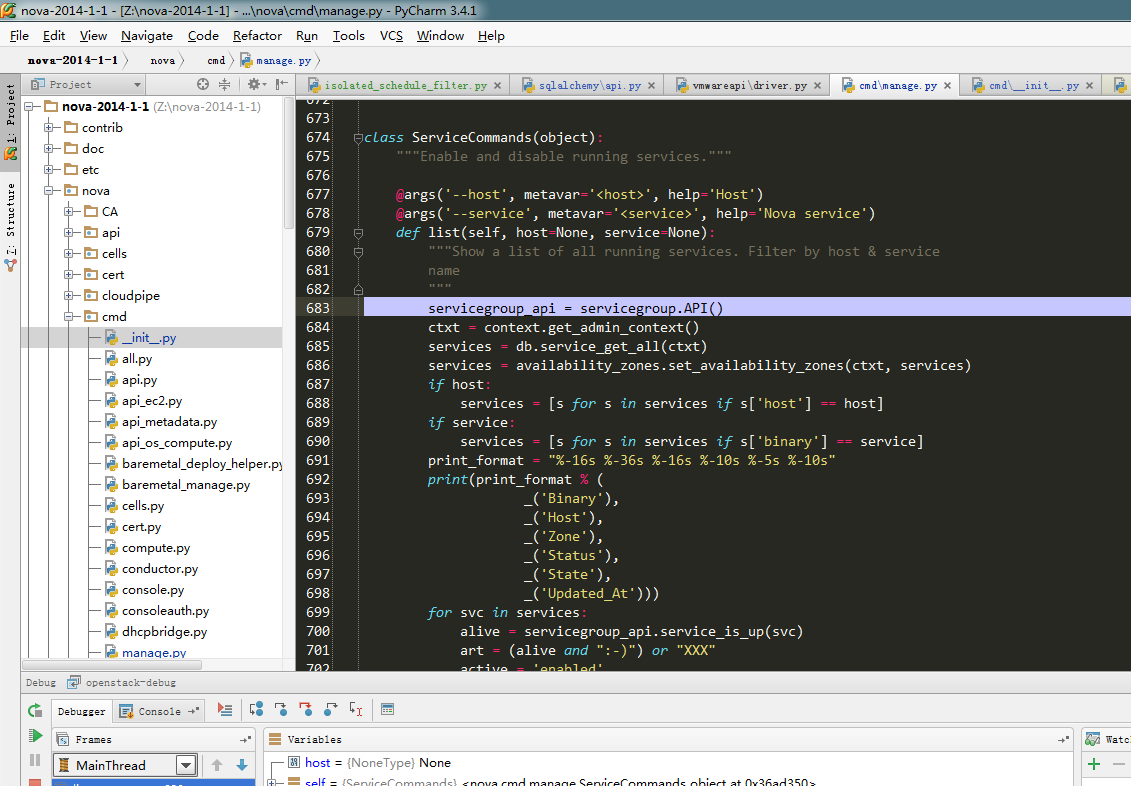
- @args('--host', metavar='<host>', help='Host')
- @args('--service', metavar='<service>', help='Nova service')
- def list(self, host=None, service=None):
- """Show a list of all running services. Filter by host & service
- name
- """
- servicegroup_api = servicegroup.API()
- ctxt = context.get_admin_context()
- services = db.service_get_all(ctxt) #获取nova service数据库表所有数据
- services = availability_zones.set_availability_zones(ctxt, services)
- if host:
- services = [s for s in services if s['host'] == host]
- if service:
- services = [s for s in services if s['binary'] == service]
- print_format = "%-16s %-36s %-16s %-10s %-5s %-10s"
- print(print_format % ( #此处打印出图1.1
- _('Binary'),
- _('Host'),
- _('Zone'),
- _('Status'),
- _('State'),
- _('Updated_At')))
- for svc in services:
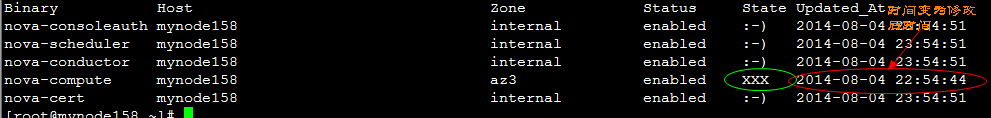
- alive = servicegroup_api.service_is_up(svc) #检测服务是否为alive 、重点解析此处的代码根据
- art = (alive and ":-)") or "XXX"
- active = 'enabled'
- if svc['disabled']:
- active = 'disabled'
- print(print_format % (svc['binary'], svc['host'],
- svc['availability_zone'], active, art,
- svc['updated_at']))
图1.1:

6、service_is_up:(根据到7讲解is_up函数)
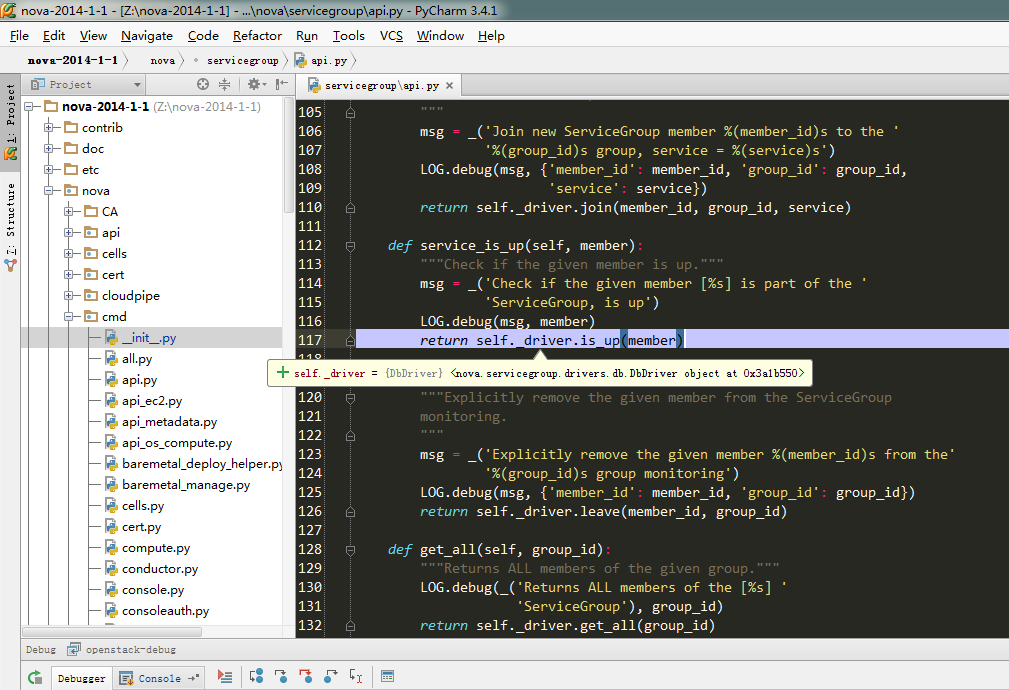
注:大家可以再下图中看到,判断服务状态,可以有多重方式,有db、还有zookeeper等。从上图可知本次中使用的为db检查服务状态。
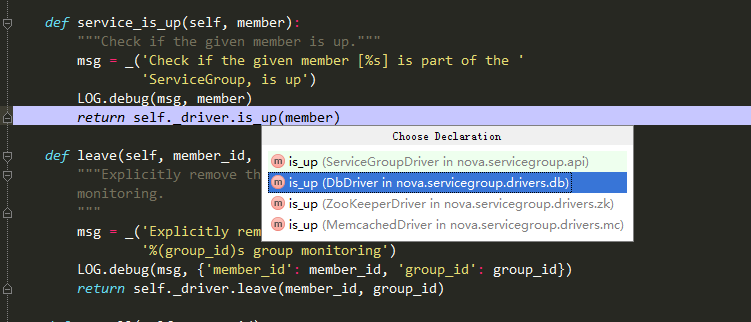
7、讲解is_up函数:
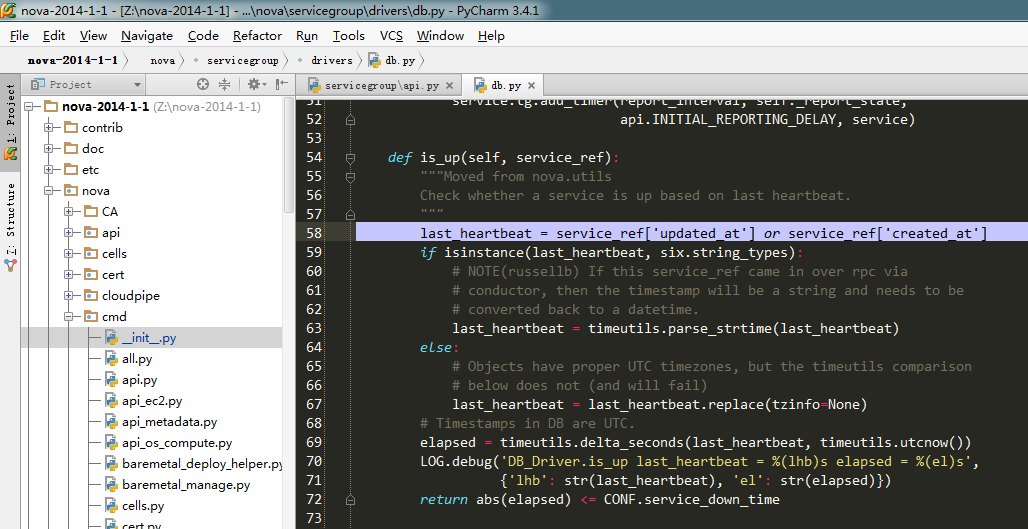
- def is_up(self, service_ref):
- """Moved from nova.utils
- Check whether a service is up based on last heartbeat.
- """
- last_heartbeat = service_ref['updated_at'] or service_ref['created_at'] #获取服务最后一次更新时间,或者第一次创建时间,最为心跳时间
- if isinstance(last_heartbeat, six.string_types): #此处代码就是将上面获取的心跳时间,转换成datetime时间
- # NOTE(russellb) If this service_ref came in over rpc via
- # conductor, then the timestamp will be a string and needs to be
- # converted back to a datetime.
- last_heartbeat = timeutils.parse_strtime(last_heartbeat)
- else:
- # Objects have proper UTC timezones, but the timeutils comparison
- # below does not (and will fail)
- last_heartbeat = last_heartbeat.replace(tzinfo=None)
- # Timestamps in DB are UTC.
- elapsed = timeutils.delta_seconds(last_heartbeat, timeutils.utcnow()) #此处计算出心跳时间与当前时间的差值
- LOG.debug('DB_Driver.is_up last_heartbeat = %(lhb)s elapsed = %(el)s',
- {'lhb': str(last_heartbeat), 'el': str(elapsed)})
- return abs(elapsed) <= CONF.service_down_time#此处根据差值来判断服务是否正常(比较时间为配置文件配置。如下图:)
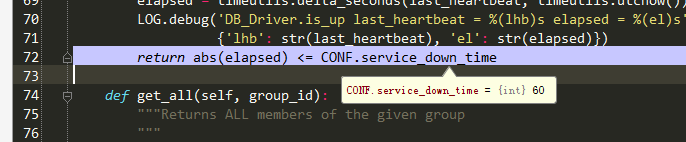
nova.conf中:
所以最近更新时间,或者第一次创建时间与当前时间间隔少于CONF.service_down_time(60秒),则认为服务alive
从这里也可以得知为什么控制节点和计算节点的时间要一致。
接下来试验验证一下:
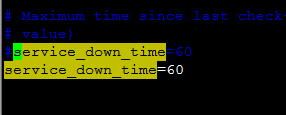
现在强制修改数据库表中nova-compute的update_at时间:
由2014-08-04 23:51:24修改为:2014-08-04 22:51:24
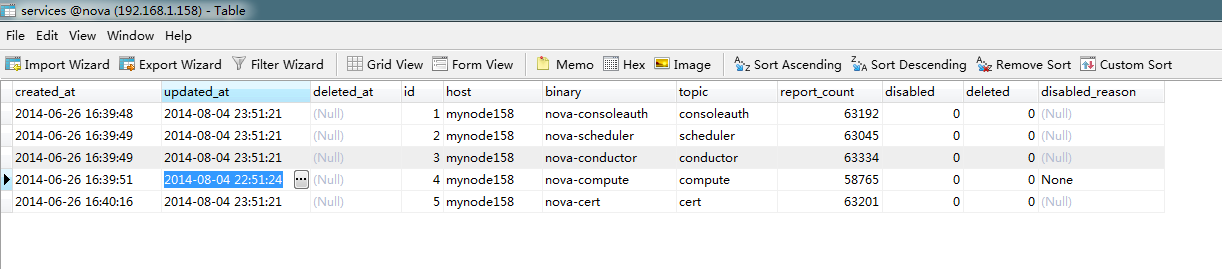
再来查看状态:
|  /2
/2 